BlueHoc simulator provides a Bluetooth extension for Network Simulator (ver 2.1b6). BlueHoc is available for download under IBM Public License (IPL) from IBM developerWorks . It requires ns-2.1b6 which can be obtained from Network Simulator site.
Bluetooth devices which are in range can discover and
connect to each other without the need of a base station or access
point. The Inquiry procdeure is used for obtaining Bluetooth addresses
and clocks of devices in range. Paging is used to connect
to devices whose addresses and approximate clock values are known.
Device disvcovery can be time consuming because the device doing inquiry
does not know the frequency and time window in which other devices might
be listening. Paging delays are much lesser because during paging
an approximate idea of the clock of the paged device (through inquiry) is available.
However, in the error-prone indoor wireless environment where inquiry and
paging exchanges could be lost over the air, both device discovery and paging
delays can be very high and unpredictable. Moreover with multiple devices doing
inquiry, the device discovery delays become even more unpredictable.
Since device disovery delays (which could be upto 10.24 sec even in an error-free
environment!) could severly affect the performance of some applications which
depend on making fast ad-hoc connections, being able to evaluate realistic delays
for an indoor wireless ad-hoc networking scenarion assumes importance.
In BlueHoc,
the inquiry and paging procedures are simulated almost exactly as in the Bluetooth
specifications. The presentation [3]
on this site describes paging and inquiry procedures briefly but for a more complete
description, refer [1], [4].
Simulation starts with
the creation of a master node and several slave nodes. The master node
starts inquiry procedure. The BThost at the master sends an
HCI_Inquiry command to the Baseband (see Figure 2). Though HCI commands are actually
packets which are transported over a physical bus, they have been
simulated as function calls. The parameters to the HCI_inquiry command
are the number of responses required and inquiry timeout. These can be
entered using the graphical interface.
In response to the HCI_Inquiry command, the Baseband starts sending Inquiry
packets with the general access code. The transmission frequency depends
upon the clock of the master and the general inquiry access code.
The slaves respond to inquiry with FHS packets which contain the device address
and the clock of the slave. When the required number of inquiry responses
are obtained (or if inquiry timeout occurs), the master starts paging the
slave assuming R1 mode (see [1]).
Some connection establishment related signaling has been simulated
in BlueHoc (see Figure 2). A group of devices consisting of a single master and upto
7 active slaves is called a Piconet. In the first version of
BlueHoc only a single piconet is considered.
LMP signaling
Once paging is over and the slave is tuned to the master hopping sequence,
Link Manager Protocol establishes an Asynchronous Connectiion-Less (ACL) link
between the master and the slave.For this the master's LMP sends a LMP_host_connection_req
to the peer LMP. When the master's LMP receives a response from the slave LMP it send an
HCI Event to BTHost indicating that the connection with the required device has (or has not)
been created. The master then sends a QoS setup command with the QoS parameters
which depend on the application for which the connection is required. For
simplicity it is assumed that there is only one flow per ACL connection. The
LMP passes on the QoS parameters to the deficit round robin based scheduler which
finds out whether the connection can be accepted or not.
L2CAP connection establishment
After the QoS negotiation at the LMP is over, it sends HCI_QoS_setup_complete_event to
BThost. The host then sends L2CA_Connect_Req to L2CAP. Signaling takes place between
L2CAP peers. Each L2CAP channel has a connection identifier (CID) associated with it. For
signaling the CID is 1. The L2CAP side which initiates connection establishment sends
an L2CAP_connection_request and the other sides sends an L2CAP_connection_response.
Through this exchange each end can identify the other end through its CID. Several
L2CAP connections can be established in this manner over a single ACL connection.
However in this version of the simulator multiple L2CAP connections over a single
ACL connection are not considered since QoS negotiation is done only once for per ACL
connection at LMP level instead of L2CAP. The L2CAP level QoS negotiation is yet to
be implemented.
QoS Mapping
QoS mapping and negotiations are done only once per ACL connection. The QoS requirements
for standard applications (like Telnet, FTP, packetized voice) are conveyed to the MAC
(scheduler) using Flow Specifications similar to RFC 1363. The Deficit Round Robin scheduler
first finds the appropriate baseband packet type to be used depending upon loss sensitivity
and application level MTU. It decides whether a connection can be admitted depending
upon current traffic level and the requirements of the connection. If admitted the connection
gets a 'quanta' of service per round robin cycle. Reservations are made only in the forward
(master to slave) direction. Though no reservation is made for the reverse side, a flow is
considered backlogged if either the forward or reverse side of the ACL link is backlogged.
The mapping used is very application specific. Currently we are looking at some uniform
mapping from the flow specification to MAC parameters. The graphical interface allows the
user to specify the application to be either FTP, Telnet or voice. The 'other' application
option is not implemented.
Note:- In the above we have assumed a likely scenario for connection establishment in
Bluetooth where the master does inquiry, paging and initiates connection establishment.
The model used for different application scenarios could be different. To implement
a different model, only the BThost implementation needs to be changed.
Logical Link Control and Adaptation Protocol Simulation
Apart from sending and receiving L2CAP_connection_req and L2CAP_connection_response,
and conveying remote CIDs, the simulated L2CAP has two main functionlities.
- Performs segmentation and reassembly (SAR) for higher layer packets.
- Implements DATA_WRITE primitive for transfer of higher layer packets over a logical
link identified by a CID.
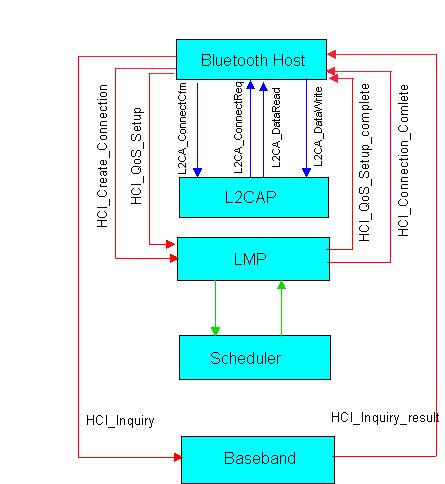
Figure 2: Connections establishment and QoS related Message Exchanges
Back
 Next
Next
BlueHoc is supported by India Research Lab

